CHEMISTRY FORM 1




- 1.1 What is matter?
- 1.2 What is Chemistry?
- 1.3 What does matter consist of?
- 1.4 Are the particles in matter stationary?
- 1.5 Arrangement, distance, and attraction between particles
- 1.6 Properties of matter (volume, shape and compression)
- 1.7 Conductors and non-conductors
- 1.8 Sources of heat
- 1.9 Bunsen burner
- 1.10 Role of Chemistry in society
- 2.1 Pure substances
- 2.2 Mixtures
- 2.3 Separation of Mixtures
- 2.4 Separation of solid-solid mixture
- 2.5 Separation of insoluble solid-liquid mixture
- 2.6 Separation of soluble solid-liquid mixture (solution)
- 2.7 Separation of immiscible liquid-liquid mixture
- 2.8 Separation of miscible liquid-liquid mixtures (solution)
- 2.9 Separation of a liquid-gas mixture
- 2.10 Selecting and using appropriate methods of separating mixtures
- 2.11 Kinetic theory of matter
- 2.12 Classification by physical states
- 2.13 Effect of heat on physical states
- 2.14 Effect of impurities on melting and boiling points
- 2.15 Permanent and non-permanent changes
- 2.16 Definitions, chemical symbols and equations

- 3.1 Simple acid-base indicators
- 3.2 Universal indicators and pH scale
- 3.3 Reactions of acids with metals
- 3.4 Reactions of acids with carbonates and hydrogen-carbonates
- 3.5 Reactions of acids with bases
- 3.6 Effects of acids on substances
- 3.7 Applications of acids and bases

- 4.1 Composition of Air
- 4.2 Fractional distillation of liquid air
- 4.3 Rusting
- 4.4 Oxygen
- 4.5 Burning of substances in air
- 4.6 Atmospheric pollution

- 5.1 Candle wax and water
- 5.2 Reactions of metals with liquid water
- 5.3 Reaction of metals with steam
- 5.4 Preparation of hydrogen gas

Acids, Bases and Indicators: Reactions of acids with carbonates and hydrogen-carbonates
3.0 Acids, Bases and Indicators 
3.4 Reactions of acids with carbonates and hydrogen-carbonates
How do acids react with metal carbonates and hydrogencarbonates?
Materials and substances required
- Copper (II) carbonate
- Hydrochloric acid
- Calcium hydroxide solution (lime water)
- Litmus paper
- Boiling tube, fitting cork, delivery tube, and a test tube
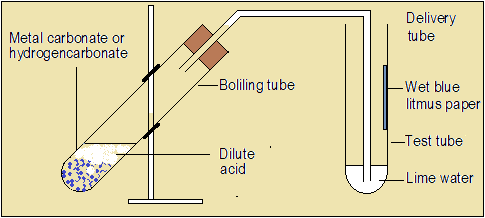
Open the video, reaction of copper (II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid.
Keenly observe what happens to the reacting mixture, lime water and blue wet litmus paper.
Questions 3.4(a)
- What is the colour of copper (II) carbonate?
- Describe the observations made when copper (II) carbonate is reacted with hydrochloric acid.
- What is the colour of the gas produced?
- What is the colour of the solution formed?
- What is the effect of the gas on lime water?
- Name the gas produced.
- What is the effect of the gas on wet blue litmus paper?
- Name the salt formed when copper and chlorine combine.
- Three products are formed in this reaction, including water. Write a word equation for the reaction.
Answers to Questions 3.4(a) 
NB: Formation of a white insoluble solid with lime water is the test for carbon (IV) oxide. No other gas affects lime water in this manner.
Other carbonates and hydrogencarbonates react with acids in a similar way to produce salt, water and carbon (IV) oxide.
Questions 3.4(b)
From the fact that other metal carbonates and hydrogencarbonates behave like copper (II) carbonate:
- Complete the table below to identify the salt solutions (a) to (f) formed when metal carbonates or hydrogencarbonates react with acids.
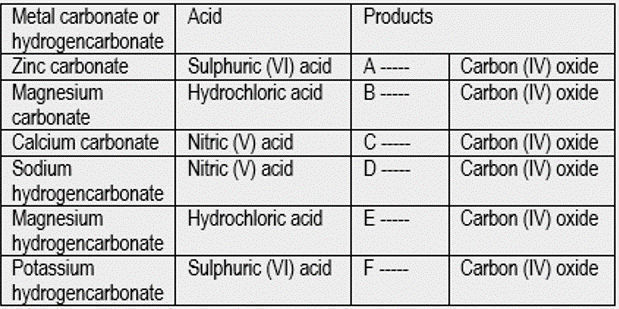
- The solid salts A to F can be obtained by evaporating their solutions to dryness or crystallization. Check and report the colour of salt A from the table of Common Chemistry Laboratory Chemicals, under zinc and its compounds.
- Describe the observations made when sodium hydrogencarbonate (a white powder) is reacted with dilute sulphuric acid.
- Write a word equation for the reaction between calcium carbonate and nitric acid.
- Write a general equation for the reaction between (a) a metal carbonate and an acid (b) a metal hydrogencarbonate and an acid.
Answers to Questions 3.4(b)
At home
Liver salt, a mixture of sodium hydrogencarbonate and citric acid, produces carbon (IV) oxide bubbles when added to water. It is taken as a remedy for acid indigestion, and neutralizes stomach acidity, as the carbon (IV) oxide produced is belched out.
NB: The two substances are chosen because they are safe for the human body.
For curiosity
The Roman numbers in brackets stand for the combining powers of elements, which will be learnt under the structure of atoms. But basically it is the number of links (bonds) through which an atom of one element combines with another element, just like we can hold one another using one hand (I) or two hands (II).
